Running a kubeflow pipeline on google vertex
This blog post will go over how to build and run your very first kubeflow pipeline (kfp). In short, Kubeflow Pipelines is a platform for building and deploying portable, scalable machine learning (ML) workflows based on Docker containers.
There are a lot of possibilities to run the pipelines, but in this series, we will use gcp vertex pipelines. Vertex will be the runner, but the pipelines will follow the kubeflow conventions meaning you can run them on whatever platform at hand or host kubeflow on your own Kubernetes cluster.
This is the first in a series of kubeflow posts and will showcase the basis; the focus is not on ML but rather how to use it. The following ones will focus more on machine learning concepts and MLOps.
Creating a basic kubeflow pipeline
First, we need to install some packages and set up Python. If you want, you can clone the repo, start the dev-container, and you can skip this step. We highly recommend this instead of spending time on your environment, as we will only cover it briefly here.
First, you need to install python:3.10, which we use in this tutorial.
Install the following packages and versions
pandas==1.5.3
kfp==2.0.0b13
ipykernel
google-cloud-aiplatform==1.23.0
python-dotenv==1.0.0
black
black[jupyter]
Most of the code will happen in a Jupyter notebook, so you also need to install Jupyter.
Setting up you gcp enviroment
The code below can be found here and the the notebook to use is first_kubeflow_pipelines.ipnyb
Create a new gcp project and add a billing account (There will be close to 0 costs here, but you need to enable it to use vertex)
Enable the following APIs; if you want to read more, you can find the information here
Compute Engine API
Vertex AI API
Cloud Storage
Create a service account with vertex AI access; an ugly way that works is to create an account that has owner access.
Ok, now it is time to start coding; the first step is to create an .env file and add the service account, the bucket name, and the gcp project
gcp_project=example-project
gcp_service_account=example-service-account@example-service-account.iam.gserviceaccount.com
bucket=gs://example-bucket
- The first step is to import the needed functions and see if we have access to list all previous run pipelines in vertex.
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
import kfp.dsl as dsl
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from kfp.v2.dsl import Output, component, InputPath, HTML, Input, Dataset
from kfp.v2 import compiler
from google.cloud import aiplatform as aip
#loading enviroment variables from the .env file
load_dotenv()
bucket = os.getenv("bucket")
gcp_project = os.getenv("gcp_project")
gcp_service_account = os.getenv("gcp_service_account")
aip.init(
project=gcp_project,
location="europe-west1",
)
all_piplines = aip.PipelineJob.list()
all_piplines
This should list all previous kfp pipelines, if your following this blog post it will probably be an empty list.
- Lets create an super simple pipeline.
def train_model(input: float) -> float:
return 2.0 + input
def ingetst_data() -> float:
return 2.0
# Create components for the ingestion and training functions
ingest_data_component = component(ingetst_data)
train_component = component(train_model)
# Define the pipeline using the Kubeflow Pipelines SDK
@dsl.pipeline(
name="ltv-train",
)
def add_pipeline():
# Instantiate the ingest_data_component and store its output
ingest_data = ingest_data_component()
# Instantiate the train_component, passing the output from the ingest_data_component
train_model = train_component(input=ingest_data.output)
# Disable caching for the train_model component to ensure it runs every time
train_model.set_caching_options(False)
# Compile the pipeline to generate a JSON file for execution
compiler.Compiler().compile(pipeline_func=add_pipeline, package_path="local_run.yaml")
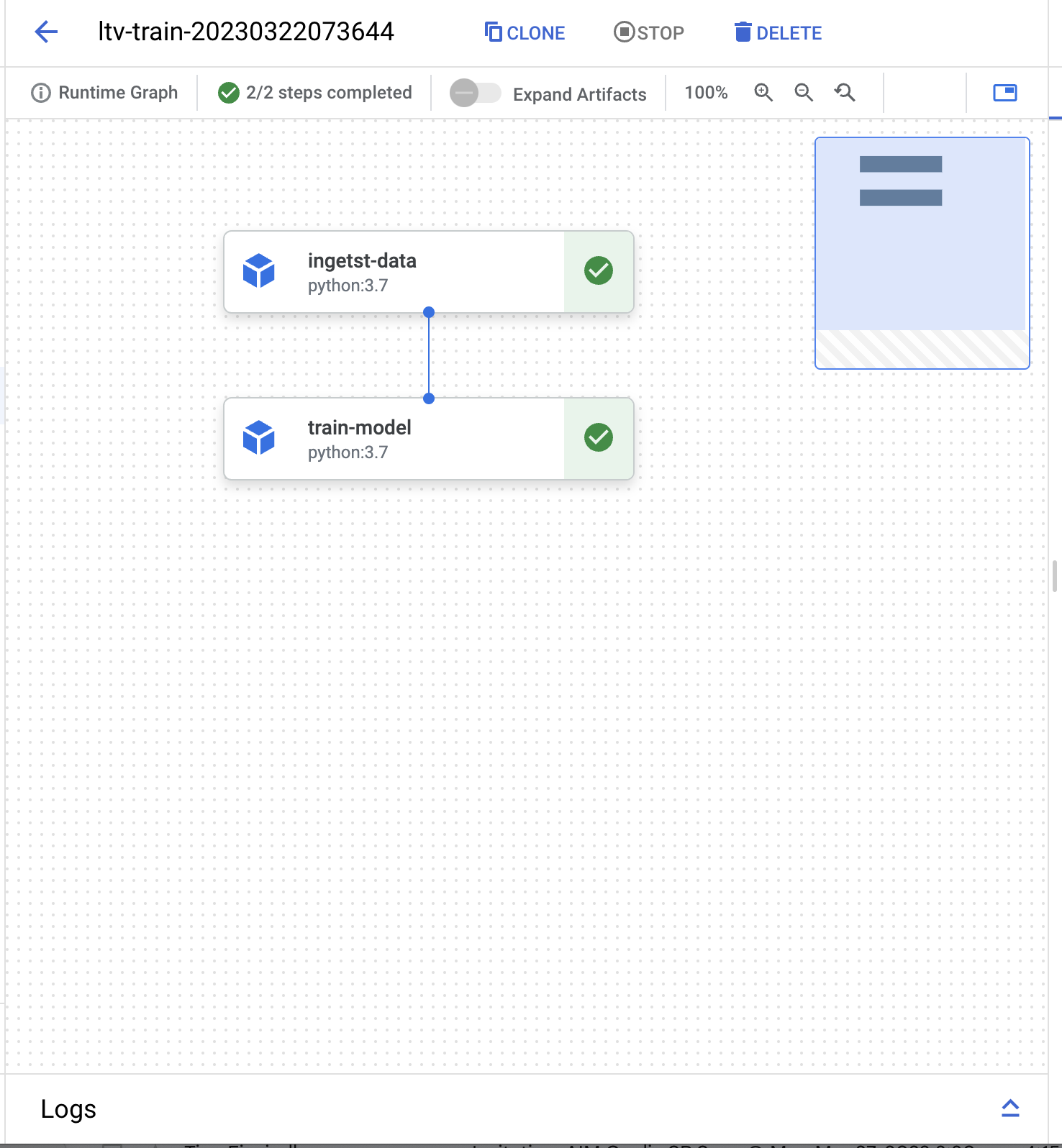
This code defines a simple pipeline using the Kubeflow Pipelines SDK. The pipeline consists of two components: a data ingestion component (ingetst_data) and a model training component (train_model). The ingetst_data component returns a constant value of 2.0, while the train_model component adds 2.0 to the input value. Finally, the pipeline is compiled and saved as a JSON file (local_run.json) for local execution or deployment.
- To execute the pipeline on vertex you run the following code
job = aip.PipelineJob(
display_name="First kubeflow pipeline",
template_path="local_run.yaml",
pipeline_root=bucket,
location="europe-west1",
project=gcp_project,
)
job.submit(
service_account=gcp_service_account
)
You should now get an output with a link the the running pipeline if you follow it you should see somthing like this.